

The enzyme reverse transcriptase transcribes RNA to generate a single strand of complementary DNA (cDNA). In reverse transcription, RNA is used as a template to produce DNA. Reverse transcription converts RNA to DNA. In addition, organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own RNA polymerases which transcribe the DNA within these cell structures.ĭNA is transcribed and translated to produce proteins.
Dna transcription and translation steps code#
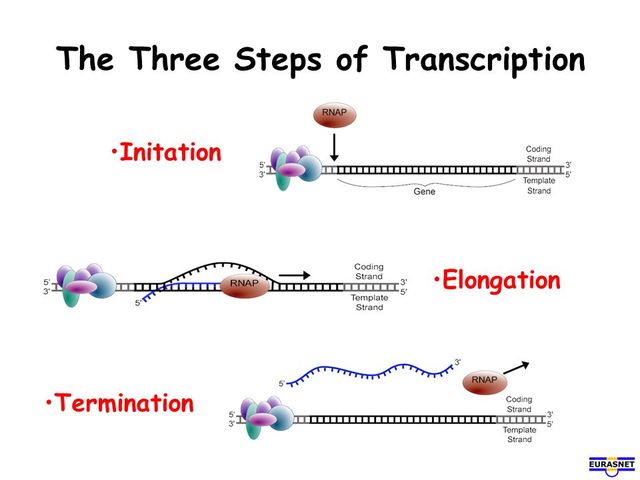
Genes that code for proteins are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, genes coding for ribosomal RNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase I, and genes that code for transfer RNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase III. In eukaryotic cells, transcription factors are needed for transcription to occur and there are different types of RNA polymerase molecules that transcribe the DNA depending on the type of genes. In prokaryotes, such as bacteria, the DNA is transcribed by one RNA polymerase molecule without the assistance of transcription factors. While transcription occurs in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the process is more complex in eukaryotes. At that point, RNA polymerase releases the mRNA polymer and detaches from the DNA.Ĭolored transmission electron micrograph of deoxyribonucleic acid, (DNA pink), transcription coupled with translation in the bacterium Escherichia coli.ĭr. Elena Kiseleva/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY/Getty Images RNA polymerase moves along the DNA until it reaches a terminator sequence. When RNA polymerase transcribes the DNA, guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C) and adenine pairs with uracil (A-U). RNA however, contains the nucleotides adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil (U). Like DNA, RNA is composed of nucleotide bases. The strand that is not transcribed is called the sense strand. The strand that serves as the template is called the antisense strand. The DNA in the promoter region contains specific sequences that allow RNA polymerase to bind to the DNA.Ĭertain enzymes called transcription factors unwind the DNA strand and allow RNA polymerase to transcribe only a single strand of DNA into a single stranded RNA polymer called messenger RNA (mRNA). RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA at a specific area called the promoter region. Specific nucleotide sequences tell RNA polymerase where to begin and where to end. Initiation: RNA Polymerase Binds to DNAĭNA is transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase.There are three main steps to the process of DNA transcription:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
